Understanding Native American treaties requires delving into the historical backdrop against which these agreements were forged. Native American tribes, with their rich cultural heritage and deep connection to the land, were central to the early development of what would become the United States. As European colonists arrived, they entered into numerous treaties with various Native American tribes. These treaties, while often framed as peaceful negotiations, frequently occurred under duress or with the power imbalance heavily favoring the colonists.
Early treaties were influenced by the colonial government’s need to acquire land for settlement and resources. These agreements were often seen as a means to avoid conflict while expanding territorial claims. Over time, however, the treaties would serve as both a foundation for legal disputes and a record of broken promises. Major historical events like the westward expansion and the establishment of the U.S. Constitution significantly impacted the nature and enforcement of these treaties.

The Legal Foundations and Significance of Native American Treaties
Native American treaties hold a unique place in U.S. law, recognized as the “supreme law of the land” under the Constitution. This legal status affirms their importance in establishing and protecting the sovereignty of Native American tribes. Sovereignty here refers to the inherent authority of tribes to govern themselves within the U.S. legal framework. The federal government’s obligations under these treaties are vast, encompassing everything from land rights to education and healthcare services.
However, the legal landscape surrounding these treaties is complex. Over the centuries, treaties have been challenged, interpreted, and often violated. The U.S. government has at times disregarded treaty provisions, leading to significant legal and social conflicts. Despite these challenges, Native American treaties continue to be a vital part of tribal sovereignty, serving as the legal bedrock for the ongoing struggle for rights and recognition.
Major Native American Treaties and Their Impacts
Several Native American treaties stand out for their profound and lasting impacts on the tribes involved. For instance, the Treaty of Fort Laramie, signed in 1851 and later in 1868, was intended to establish peace between the U.S. and various Plains tribes. Yet, its terms were frequently violated, leading to continued conflicts and the eventual loss of vast tracts of tribal land.
Similarly, the Treaty of New Echota (1835) led to the infamous Trail of Tears, where thousands of Cherokee were forcibly relocated from their ancestral lands. This event underscores the harsh realities many tribes faced when treaties were not honored. Other treaties, like those signed with the Navajo and Sioux, also resulted in significant loss of land and cultural disruption.
Each of these treaties holds a unique place in history, illustrating the broader pattern of broken promises and the enduring impact on Native American communities. Understanding these treaties helps shed light on the historical struggles that continue to shape the lives of Native Americans today.
Common Violations and Challenges of Native American Treaties
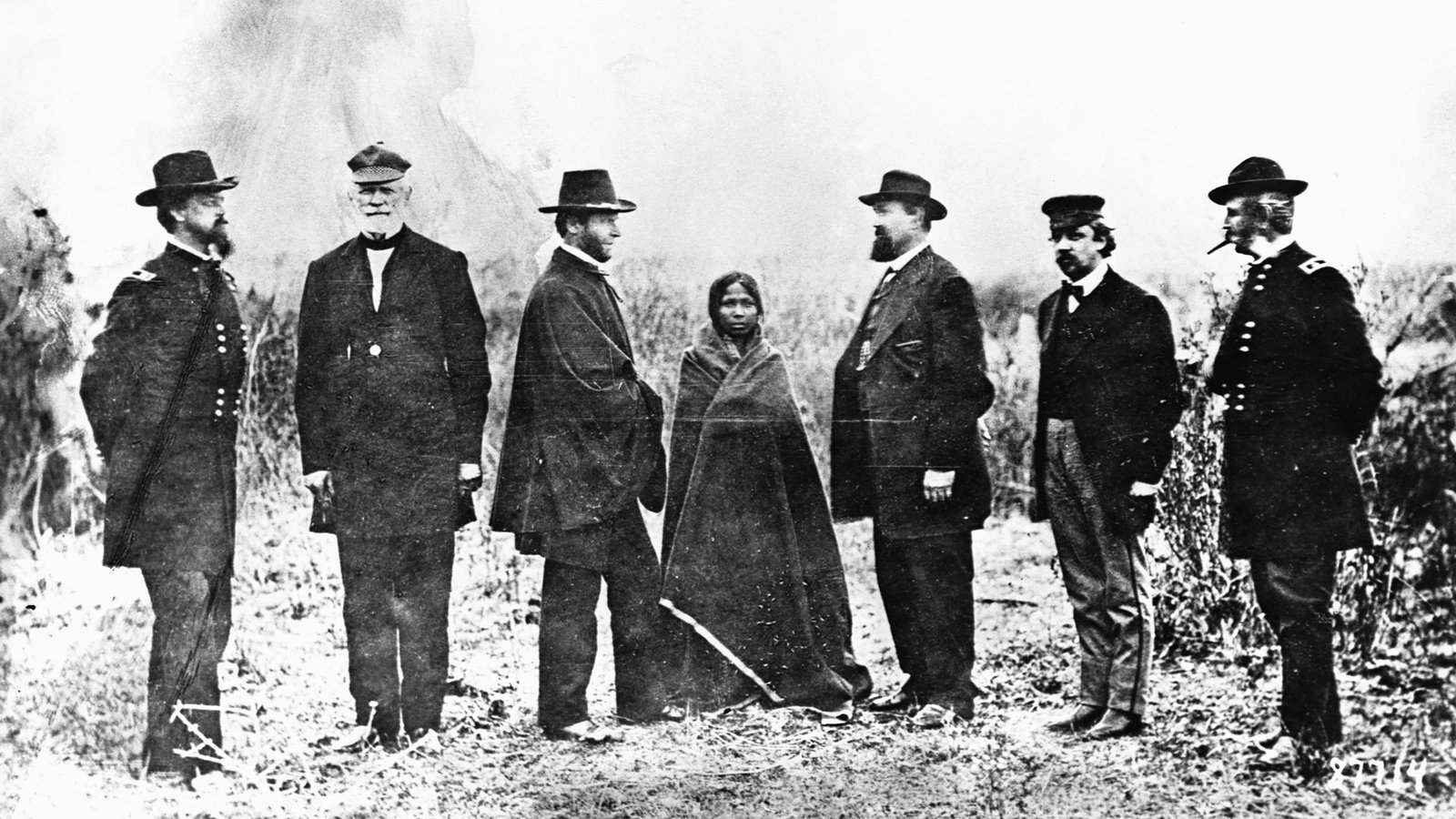
Throughout history, Native American treaties have been subject to numerous violations by the U.S. government. These violations range from outright disregard for treaty terms to more subtle infringements, such as inadequate resource allocation or failure to honor land rights. One notable example is the illegal seizure of the Black Hills, sacred to the Sioux Nation, despite the land being guaranteed under the Treaty of Fort Laramie.
Legal battles have ensued over these violations, with tribes often having to fight in court to uphold their treaty rights. These court cases highlight the ongoing struggle for justice and recognition. For instance, in 1980, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that the seizure of the Black Hills was illegal, awarding the Sioux Nation monetary compensation. However, the Sioux have refused the money, insisting on the return of their land instead.

The challenges of enforcing Native American treaties are compounded by the evolving nature of federal Indian policy. As policies shift, so too does the interpretation and implementation of treaty obligations, often to the detriment of Native American tribes.
Modern Interpretations and Applications of Native American Treaties
Today, Native American treaties continue to influence legal and political landscapes, particularly in disputes over land and resources. Modern interpretations of these treaties often revolve around the principle of tribal sovereignty and the federal government’s trust responsibility. This responsibility includes ensuring that treaty rights are upheld and that tribes receive the resources promised to them.
Recent Supreme Court rulings have reaffirmed the importance of Native American treaties in modern law. For example, the 2020 McGirt v. Oklahoma decision recognized that much of eastern Oklahoma remains Native American land under the terms of an 1833 treaty. Such rulings have far-reaching implications, affecting everything from criminal jurisdiction to land use.
In the current legal framework, Native American treaties are not just historical artifacts; they are living documents that continue to shape the relationship between the U.S. government and Native American tribes.
The Future of Native American Treaties
Looking ahead, the future of Native American treaties involves ongoing efforts to renegotiate, reaffirm, or even reimagine treaty rights. Tribal leaders play a crucial role in these discussions, advocating for the protection of their rights and the fulfillment of treaty obligations. Modern legislation, such as the Indian Self-Determination Act, has empowered tribes to take a more active role in managing their affairs, further emphasizing the importance of treaties.

However, challenges remain, particularly in areas like environmental protection, land use, and cultural preservation. As the U.S. continues to evolve, so too must its approach to honoring Native American treaties. The future will likely see a continued push for greater autonomy and recognition of tribal sovereignty.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Native American Treaties
In conclusion, Native American treaties are not merely historical documents; they are foundational to the identity, rights, and sovereignty of Native American tribes. These treaties have shaped the past and continue to influence the present and future. Upholding these treaties is not just a legal obligation but a moral one, essential to preserving the rich cultural heritage and autonomy of Native American peoples.
Understanding the history, legal foundations, and ongoing significance of Native American treaties is crucial for anyone interested in the rights and history of Native Americans. As we move forward, it is vital to ensure that these agreements are respected, honored, and fully implemented.
FAQs about Native American Treaties
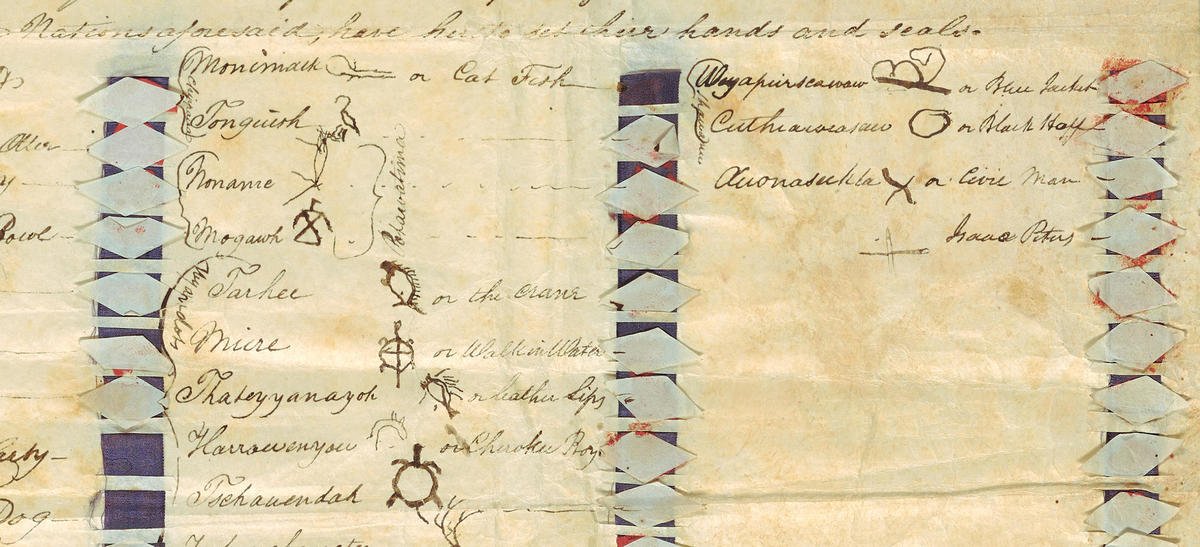
What is the significance of treaties between Native American tribes and the U.S. government?
Treaties between Native American tribes and the U.S. government are legally binding agreements that established the terms of relationships between sovereign nations. These treaties often involved the ceding of large portions of tribal lands to the U.S. in exchange for promises of protection, resources, and rights. The significance of these treaties lies in their recognition of tribal sovereignty and the establishment of a nation-to-nation relationship. However, many treaties were later broken or altered by the U.S. government, leading to long-term negative impacts on Native communities.
How do treaties impact tribal sovereignty today?
Treaties continue to play a critical role in upholding tribal sovereignty, which is the inherent authority of Indigenous tribes to govern themselves. These agreements reinforce the tribes’ right to self-governance, including managing their lands, resources, and internal affairs independently from state or federal government interference. The U.S. government still recognizes these treaties, affirming the unique political status of Native American tribes as distinct sovereign entities within the United States.
Are Native American treaties still legally binding?
Yes, Native American treaties are still legally binding under U.S. law. Even though the practice of treaty-making with tribes officially ended in 1871, existing treaties remain in effect unless they have been specifically altered or abrogated by legislation. The U.S. Supreme Court has consistently upheld the validity of these treaties, recognizing them as the “supreme law of the land” as stated in the Constitution.
What are the ongoing challenges related to treaty rights?
One of the ongoing challenges related to treaty rights is the enforcement and protection of the rights guaranteed to Native American tribes under these agreements. Many tribes face legal battles to ensure their treaty rights are honored, particularly in areas like land use, natural resource management, and hunting and fishing rights. Additionally, there is often a need for continuous negotiation and advocacy to address violations and to adapt treaty terms to modern contexts.
How do treaties affect land ownership among Native American tribes?
Treaties often resulted in the cession of vast amounts of tribal land to the U.S. government. However, many treaties also reserved certain lands for tribes, known as reservations, where tribes maintain a level of sovereignty and control. The issue of land ownership is complex, as treaties have historically been manipulated or broken, leading to the loss of tribal lands. Today, some tribes are working to reclaim or protect their remaining lands through legal avenues and negotiations.